
E-cigarettes are battery-powered electronic devices that heat a liquid that often contains nicotine, artificial flavors, and other substances such as propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin. This liquid turns into a spray that is inhaled through the device. The term "Vaping" is used to refer to the process of inhaling this spray.
E-cigarettes have gone through four generations over time, and these generations vary in their design and use:
1. The first generation: simple, disposable devices designed to mimic traditional cigarettes.
2. The second generation: rechargeable devices that contain cartridges that can be refilled.
3. The third generation: known as "Mods" devices, and are characterized by their ability to adjust the voltage and other settings according to the user's desire.
4. The fourth generation: "Pod Mods" devices, which are smaller and more advanced, and use nicotine salts instead of traditional nicotine, making inhalation less irritating to the throat and more impactful on health.
E-cigarettes contain several basic components, each of which has potential health effects:
· Nicotine: A highly addictive substance that negatively affects cardiovascular health, causing increased heart rate and blood pressure, and is associated with changes in blood vessel function.
· Propylene glycol and glycerin: They are used as moisturizers to produce the spray, but inhaling them in large quantities may lead to respiratory irritation and respiratory problems.
· Flavors and sweeteners: These substances add appeal to the product, but they may be toxic when heated, leading to respiratory infections.
· Heavy metals: such as nickel and chromium, which are sometimes released during use, increasing the risk of cancer and respiratory and heart diseases.
Studies indicate that there are acute and chronic health effects resulting from the use of e-cigarettes:
1. Acute effects:
· High blood pressure and increased heart rate.
· Circulatory disorders and impaired vascular function.
· Respiratory irritation and damage to lung cells.
2. Chronic effects:
· Risk of cardiovascular disease.
· Possibility of developing chronic inflammation and complications in the lungs.
· Accumulation of toxic substances and heavy metals in the body over time, thus causing malignant cancers.
Despite expectations that electronic cigarettes would achieve health goals to reduce the harms of smoking, they have not effectively achieved this goal. The number of traditional tobacco smokers has decreased, but the number of e-cigarette users has increased significantly, leading to an increase in addiction cases. The result is that tobacco and e-cigarette companies have made their profits, while millions of people have lost their health.
Prepared by Dr. Moaz Mohammed Moataz Al-Mahaini.
Sources and references:
1. Isik Andrikopoulos G., Farsalinos K., Poulas K. (2019). "Electronic nicotine delivery systems (ENDS) and their relevance in oral health." Toxics, 7(4):61. DOI: 10.3390/toxics7040061.
2. Farsalinos K.E., Romagna G., Tsiapras D., et al. (2014). "Characteristics, perceived side effects, and benefits of electronic cigarette use: a worldwide survey." Int J Environ Res Public Health, 11(4):4356-73. DOI: 10.3390/ijerph110404356.
3.U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. (2016). “E-Cigarette Use Among Youth and Young Adults: A Report of the Surgeon General.” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
4. Jason J. Rose, Suchitra Krishnan-Sarin, Vernat J. Exil, et al. (2023). “Cardiopulmonary Impact of Electronic Cigarettes and Vaping Products.” Circulation. DOI: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001160.
5. David Bernhard et al. (2024). "Vaping Versus Smoking: Are Electronic-Cigarettes the Savior?" Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 44(5):1012-1015. DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.123.319575.
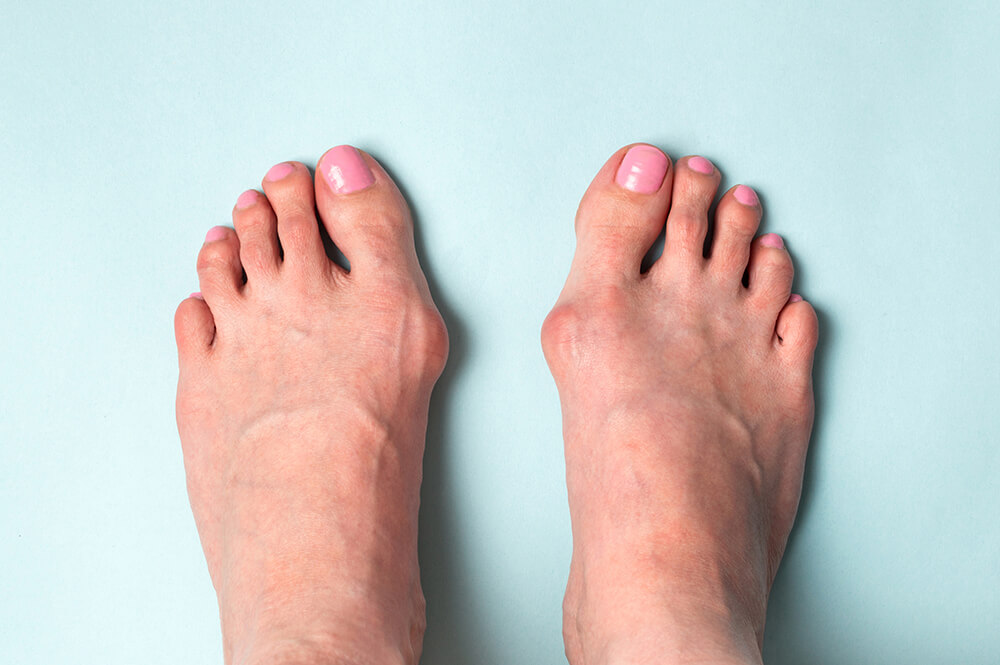
Perhaps the most important thing that attracts attention in shoe shopping stores is high heel shoes, but have you ever wondered about the dangers and health disadvantages related to them?
High heels and tight shoes cause many back and feet pains, in addition to causing many deformities, of which the hallux valgus is the most common.
It is a pathological condition in which a bony protrusion appears on the joint at the base of the big toe, which leads to its deviation towards the rest of the toes.
Women are more likely to suffer from this deformity, as a result of wearing tight shoes and high-heeled shoes, in addition to the presence of other factors that predispose to infection, such as the genetic factor, obesity, flat feet, and some chronic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
This condition leads to many symptoms whose severity varies according to the degree of deformity, starting with mild pain to reach inflammation and defective deformation in the shape of the foot, which leads to chronic pain that accompanies the patient throughout his life.
Management of this condition requires two types of treatments:
One of them is pain relief using NSAID's and corticosteroid injections.
And the other is by using physical therapy, wearing flexible shoes, and reducing excess weight. In some severe cases, we may have to perform surgery in order to relieve the patient from the severe pain he suffers from. To prevent the occurrence of injury or to reduce its severity, it is recommended to follow the following instructions:
Prepared by Dr.: Moaz Muhammad Moataz Al-Mahaini.
Linguistic proofreading: Lana Muhammad Moataz al-Mahaini.
Bunion. (n.d)
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0002211/
Bunions. (2012, September)
orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=a00155
Bunions (hallux abducto valgus). (n.d.)
foothealthfacts.org/footankleinfo/bunions.htm
Mayo Clinic Staff. (2014, February 11). Bunions
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/bunions/home/ovc-20262028
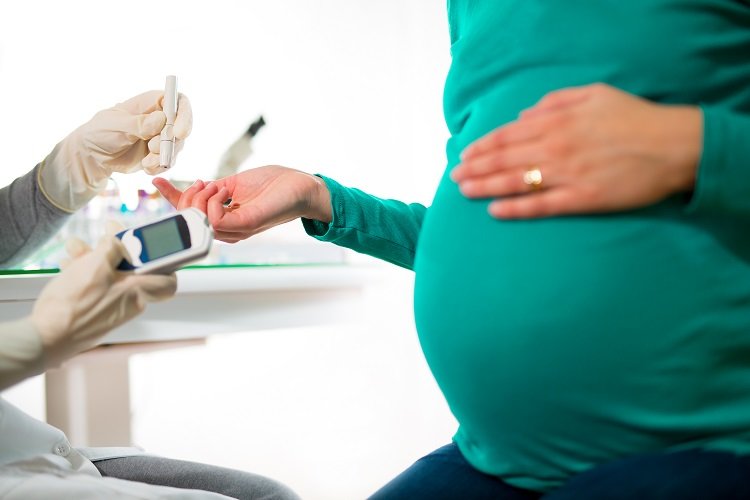

Gestational diabetes is defined as diabetes that occurs during pregnancy and is characterized by an increase in the blood sugar levels of the expectant mother. Gestational diabetes is one of the most important health problems facing pregnant women, and its proper diagnosis and treatment is vital for the health of the mother and fetus.
Gestational diabetes occurs when hormonal production increases in the body of the expectant mother, which leads to increased levels of sugar in the blood. This is caused by the inability of the pancreas to produce enough insulin, which is required to convert sugar into energy. And the high level of sugar in the blood affects the development of the fetus and the health of the expectant mother.
The reasons can be genetic, as the chances of developing gestational diabetes increase in women who have diabetes in their families. Excess weight, an unhealthy diet, and an inactive life also increase the risk of gestational diabetes.
Some people feel that there are no symptoms of gestational diabetes, but in some cases symptoms can include:
Although these symptoms aren't always obvious, they warrant blood sugar levels for a diagnosis of gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes can be prevented through lifestyle changes, such as:
Treatment options for gestational diabetes vary according to each case, and treatment includes:
Gestational diabetes is usually diagnosed by checking blood sugar levels after eating breakfast, and in pregnant women, this test should be done periodically during pregnancy. The primary test for gestational diabetes is the oral glucose tolerance test, in which the blood glucose level is checked after a specific amount of glucose is consumed. If blood sugar levels are high, gestational diabetes is diagnosed.
Failure to properly manage gestational diabetes may lead to serious complications during pregnancy and childbirth, including:
Therefore, pregnant women with gestational diabetes have to follow up their condition regularly with their physician and follow a healthy lifestyle and appropriate treatment to avoid these potential complications.
Gestational diabetes can be prevented through lifestyle changes, such as:
Treatment options for gestational diabetes vary according to each case, and treatment includes:
Ultimately, expectant mothers must carefully monitor their condition and seriously deal with gestational diabetes, which can lead to serious complications for the mother and fetus. A healthy lifestyle and appropriate treatment should be adhered to to prevent these complications and ensure the health of the mother and fetus.

سرطان البوستات
شهر نوفمبر شهر التوعية
بواحد من أكثر السرطانات انتشاراً عند الذكور وهو سرطان البروستات
هي غدة تقع أسفل المثانة
أمام المستقيم عند الذكورنمو خلايا هذه الغدة بشكل غير طبيعي وخارج عن السيطرة هو
سرطان البروستات
غالباً هذا السرطان بطيء
النمو و يمكن علاجه بنجاح فقط عند الكشف المبكر عنه بالمراحل الأولى.
ولازم يتفرق عن حالة تسمى
تضخم البروستات الحميد وفيها يكون تضخم أو تكاثر الخلايا حميد.
يمكن إن يكون سرطان
البروستات بدون أعراض و لا تظهر إلا في مراحل متقدمة أو عند انتشاره للعظام في
الحوض أو الفقرات أو الأضلاع
أعراض
سرطان البوستات
- مشكلات
التبول صعوبة التبول و حرقة أو ألم عند التبول
- الحاجة
المتكررة للتبول خاصة في الليل
- ضعف
تدفق البول أو عدم قدرة مفاجئة على التبول
- وجود دم
في البول أو السائل المنوي
- ألم عند
الجلوس إذا كانت الغدة متضخمة
- ضغف
الأداء الجنسي
- فقدان
الشهية
- فقدان
الوزن غير المبرر
- تعب
مستمر
- آلام
شديدة في العظام أو أسفل الظهر أو أسفل الحوض أو بالخصيتين
- وذمة و
تورم بالساقين
- تغيرات
بحركة الأمعاء
- الفحص
الإصبعي للمستقيم
- الكشف
عن المستضد البروستاتي النوعي PSA
- تصوير
الإيكو
- الخزعة
و هي المؤكد النهائي
العلاج
تتنوع خيارات العلاج فتوجد أكثر من طريقة واحدة و اختيار الطريقة الأفضل يكون لكل
حالة بذات
حسب انتشار السرطان و سرعة
نموه و عمر المريض و عوامل أخرى يحددها الطبيب .ومن
الخيارات العلاج الإشعاعي أو الهرموني أو الاستئصال الجراحي .
- العمر
تزيد خطورة الإصابة عند يتجاوز عمر الرجل 50 عاماً
- التاريخ
العائلي تزداد الخطورة عند وجود إصابة واحدة أو أكثر في العائلة
- مستويات
عالية من هرمون التستوسترون بسبب مرضي أو بسبب الأدوية
لا يمكن منع الإصابة بسرطان البروستات لكن تقليل من مضاعفته ومخاطره من خلال الكشف
المبكر و ذلك وجود أي عامل من عوامل الخطر .
كيف أمنع سرطان البروستات أن يتطور
وهناك بعض التدابير التي
يمكن اتباعها للحد من تطور المرض مثل:
التغذية الصحية
النشاط الجسدي المنتظم
وهكذا نرى أنّ سرطان
البروستات على الرغم من انتشاره الكبير إلا أن الكشف المبكر عنه يقلل الكثير من
النتائج المحتملة.
إعداد
الدكتورة وئام الشقران

هل تعلمون أن سرطان الثدي هو أكثر أنواع السرطانات شيوعاً بين النساء حول العالم، وهل تعلمون أنه يمكن الوقاية من مضاعفاته و الشفاء منه إذا تم اكتشافه مبكراً⁉
في شهر أكتوبر من كل عام، نحتفل بالشهر الوردي ، وهو حملة عالمية لزيادة التوعية بسرطان الثدي وتشجيع المرأة على فحص ثديها بانتظام وطلب المساعدة الطبية إذا لاحظت أي تغيرات غير طبيعية.
ما هي علامات وأعراض سرطان الثدي
سرطان الثدي هو نمو غير طبيعي لخلايا الثدي، وقد يسبب بعض التغيرات في شكل وحجم وملمس الثدي أو الحلمة أو الجلد المحيط بها
بعض العلامات والأعراض المحتملة لسرطان الثدي هي :
-وجود كتلة أو عقدة صلبة في الثدي أو تحت الإبط.
-انتفاخ أو تورم في جزء من الثدي.
- تغير في حجم أو شكل الثدي.
-تجعد أو تقشر أو تساقط للجلد على الثدي أو الحلمة.
-انعكاس أو انقلاب لحلمة الثدي.
-خروج إفرازات من الحلمة، قد تكون دموية أو شفافة.
-آلام في الثدي أو الحلمة.
-احمرار أو حرارة أو التهاب في الثدي.
-ظهور طفح جلدي على الثدي مشابه لالتهاب الجلد.
ما هي عوامل الخطر للإصابة بسرطان الثدي؟
بدايةً مفهوم عامل الخطر هو أي شيء يزيد من احتمالية حدوث مرض معين، وفي حالتنا هذه هو سرطان الثدي .
بناءً على ذلك تقسم عوامل الخطورة للإصابة بسرطان الثدي إلى قسمين :
القسم الأول وهي العوامل التي لا تتمكن السيدة من التحكم بها مثل:
الجينات
التاريخ العائلي أي إذا كانت المرأة لديها قريبة من الدرجة الأولى (أم، أخت، ابنة) قد اصيبت بسرطان الثدي، فإن خطر إصابتها يزداد .
التعرض المتكرر للإشعاع على منطقة الصدر في عمر مبكرة .
بدء الدورة الشهرية بعمر مبكر.
القسم الثاني وهي العوامل التي تتمكن السيدة من التحكم بها و
تستطيع من خلالها محاربة السرطان:
-العناية بالذات و اتباع نظام حياة صحي
-تناول الطعام الصحي والتخلص من الوزن الزائد
-الابتعاد عن التدخين والمشروبات الكحولية.
-ممارسة الرياضة لمدة 30 دقيقة يومياً
-الإنجاب والاهتمام بالرضاعة الطبيعية لأنها تعد من العوامل الهامّة لمحاربة سرطان الثدي.
كيف يمكن فحص الثدي بشكل صحيح؟
الفحص الذاتي للثدي وهو يعد من أهم طرق الكشف الدورية المتناولة بيد جميع السيدات لسهولة تطبيقها
يقسم الفحص الذاتي للثدي إلى ثلاث خطوات ولكل خطوة وضعية يتم من خلالها تحري نسيج الثدي بشكل كامل :
الخطوة الأولى تكون أثناء الاستحمام بحيث يكون الجلد رطب وزلق يتم فيها وضع اليد اليسرى خلف الرأس وفحص الثدي الأيسر بأصابع اليد اليمنى بنعومة للبحث عن أي كتل وعلى العكس للثدي الأيمن .
الخطوة الثانية تكون أمام المرآة بوضع اليدين على الخصر و تأمل الثدي وملاحظة التناظر وأي تغير في شكل أحد الثديين ونكرر العملية ولكن برفع اليدين إلى الأعلى وماننسى أنو من الطبيعي يكون في فرق بسيط بحجم الثديين ولا يعتبر مرضي .
الخطوة الثالثة تكون بوضعية الاستلقاء على الظهر و وضع وسادة أو منشفة تحت الكتفين و وضع اليد اليسرى خلف الرأس وفحص الثدي الأيسر باليد اليمنى وعلى العكس لفحص الثدي الأيمن وبهذه الطريقة ينفرد كامل نسيج الثدي على جدار الصدر ويسهل اكتشاف الكتل.
طبعاً الفحص الذاتي للثدي يتم تطبيقه مرة واحدة كل شهر بعد انتهاء الدورة الشهرية ب 7 أيام
أما بالنسبة للسيدات بسن اليأس فهو كمان مرة واحدة ولكن بيوم ثابت من كل شهر.
ولبيان أهمية هذا الفحص يجب أن ننوه على أن الإحصائيات تشير إلى أن 40%‼من سرطانات الثدي التي يتم اكتشافها تكون من قبل السيدات خلال إجرائهن للفحص الذاتي .
سرطان الثدي لا يعني النهاية هناك الكثير من النساء اللواتي تغلبن على هذا المرض وأمضين حياة طبيعية وسعيدة كوني إحداهن ولا تستسلمي للخوف أو الإحباط اطمئني فأنت لست وحدك في هذه المعركة نحن معك وندعمك ونحبك
إعداد الدكنور معاذ المهايني
Egg freezing is a method used to preserve reproductive capacity in women.
First, the eggs are extracted using anesthesia, and the egg extraction process usually takes place in the attending physician’s office.
Vaginal aspiration of eggs using ultrasound is a common method of egg retrieval.
An ultrasound probe is inserted transvaginally to locate the follicles, then a small needle is inserted transvaginally to guide it into the vagina, and the eggs are aspirated and the egg is extracted within 15 to 20 minutes. The woman may feel colic and bloating after the eggs are extracted, and the symptoms will disappear within two weeks at most.
After extracting the eggs, they are cooled to a temperature below zero, in order to stop the biological activity of the eggs, and to preserve the eggs for future use. However, pregnancy rates using frozen eggs are lower than the natural chances of pregnancy.
You should prepare for egg freezing, as follows:
From this stage, the process takes a minimum of three weeks, according to the British National Health Service website:
Egg freezing may be an option if a woman is not ready to become pregnant now, or wants to have a child in the future. Unlike embryo freezing, egg freezing does not require sperm for fertilization, because the egg will not be fertilized before it is frozen, but you will only need some medication to stimulate ovulation.
The most important reasons are if the woman is about to undergo cancer treatment, or is taking any other treatment that may affect fertility in the future. Some medications, such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy, may significantly affect fertility.
There are small, but still present, risks associated with the different stages of the operation:
When the owner of the eggs decides to use them, they are extracted from the frozen state, and each one is examined to see what is suitable for use.
It is used in the same way as ICSI, as it fertilizes the egg with a sperm, then implants it in the uterus to start pregnancy. The fertilization process is not linked to a specific age, as the uterus is not affected by age, but the ovary.
The process gives a great deal of hope to women who want to preserve their chances of having children without being restricted to a certain age, but it does not guarantee a high success rate.
Success rates range from 30-60 percent, depending on the woman's age when the eggs were collected and the period during which they were frozen.
Prepared by: Hassan Al-Aqla